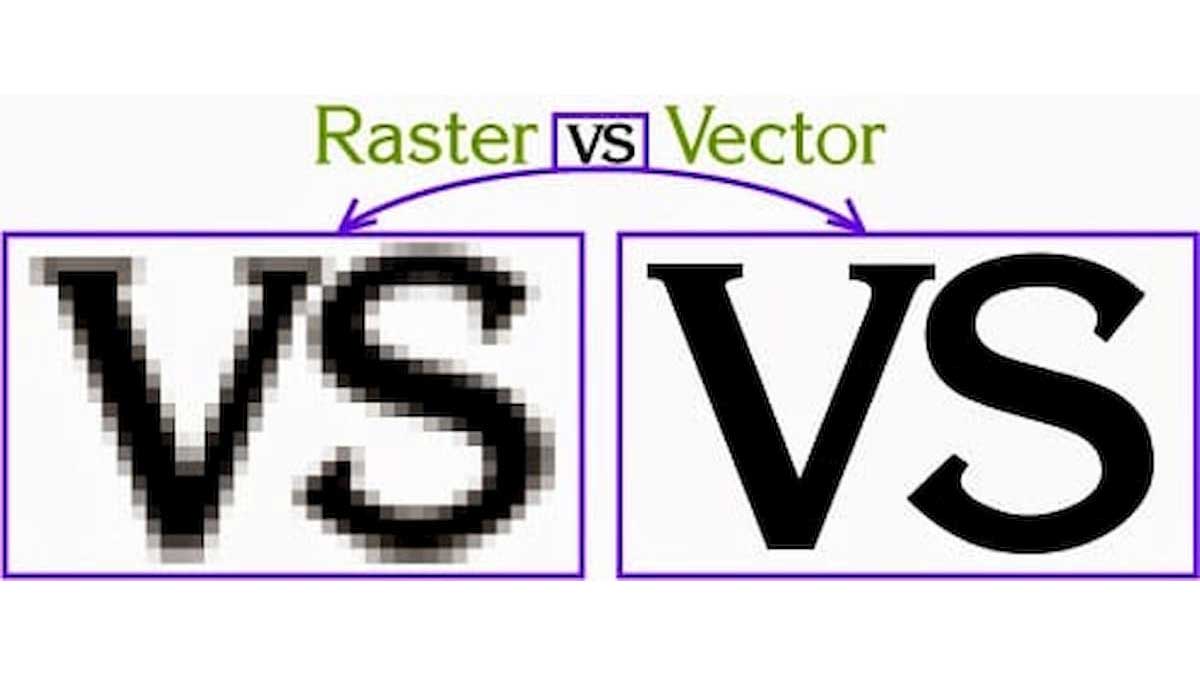
It adds many 3D CAD file formats for storing and transmitting data. CAD file formats are classified in terms of two distinct forms. It offers bitmap or raster format and the vector format. The distinction clarifies the two formats by pointing out the critical difference between them.
The raster format adds images in terms of pixels. On a display monitor, the pixels work as dots that carry colour attributes and levels of intensity in RGB. Raster graphics are suitable for photographic images adding resolution-dependent. One does not need to scale higher resolutions without loss of quality. It uses an image that is grainier by adding image details. The vector format represents images as lines, points, curves and polygons on an algebraic grid. The primitives are utilised to create vector-based images. It scales up to any resolution without loss in quality.
Raster Image Formats in CAD
The essential difference between raster and vector-based images covers raster images when scaled higher than the resolution we create. On the other hand, vector images are scaled up or down without any loss in image quality:
- Popular raster-based formats include JPEG, PNG, BMP, and TIFF.
- Popular vector-based formats add EPS, PDFor AI, SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics), WMF (Windows Metafile Format), DXF (Drawing Exchange Format), DRW, and DWG formats.
- Compound formats come with EPS, PDF, SWF, and PICT and contain pixel and vector-based data.
Raster Image Formats in CAD
It determines whether the raster image format disappears from CAD file systems. This article answers all specific questions:
- How popular is vector format based on leading CAD vendors?
- Which CAD file formats come with 3D printing technology?
- Is any particular CAD file format suited for CAD data exchange?
- Why raster format remains an essential part of CAD file systems?
HOW POPULAR IS VECTOR FORMAT AMONG LEADING CAD VENDORS?
It offers modern CAD software packages storing design and drawing information in vector format. To confirm this observation, it’s worthwhile to look at CAD formats that lead to CAD vendors, such like:
- AutoDesk is used as its native file format, supporting DWG, DXF and more.
- AutoCADuses the DWG and DXF vector formats.
SolidWorks mainly uses a structured format in which different file formats are embedded. The design data are stored in the DXF vector-based formats covering AI, GCR, and STL. It keeps in a structured layout. The structured format also holds raster formatted images.
Many software applications can convert images between the raster and vector formats. It adds significant images that convert CorelDRAW, Easy Trace, WiseImage, Freehand, VP Software, and others. It leads to CAD vendors that convert between raster and vector file formats.
WHICH CAD FILE FORMATS ARE MOST FAMOUS FOR 3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY?
The format used for 3D printing comes with STL (STereoLithography) format. We aren’t sure whether any CAD file format is most suitable for 3D printing. It leads to 3D companies, including Stratasys and 3D Systems, that convert automatically into recognisable CAD files. Further, CAD vendors export their files into STL, including Catia, Autodesk Inventor, SolidWorks, SolidEdge and ProEngineer.
IS THERE ANY PARTICULAR CAD FILE FORMAT BEST SUITED FOR CAD DATA EXCHANGE?
There is no answer to this question. The CAD file exchange software will have the ability to convert between raster and vector formats. The reason requirement comes with a modern CAD file system. It moves towards a structured file format that works better in which both raster and vector file formats are embedded. The contemporary CAD files contain more drawings and design information. It makes sense to come with different file formats stored within a structure adding minimal information lost during file transmissions.
An excellent example is integrating different data types into a CAD file offered by BIM (Building Information Modelling). BIM helps incorporate activities for parties and disciplines involved in a building project. It comes with a synergistic body that exchanges different information types. With other teams working together on a project, it needs to use different file formats that add information exchange.
Also, the Raster formats need visual displays, virtualisation and animation. It’s vector formats that use design drawings which is scalable. BIM offers a valuable extension on the CAD file format that’s not recognised as a CAD file format. The complexities integrate CAD file formats adding necessary coin a different acronym for a unified file format that does not primarily contain CAD information.
The answer to the question “Is any CAD file format best suited for CAD data exchange?” is no, with qualifications. If the CAD data is exchanged strictly in design drawings, the vector format is best suited for the data exchange. It comes with scalability and without loss of data information. The CAD data is exchanged strictly in pictorial views or animation. Then the raster format, created with a high enough resolution, works best suited for the data exchange.
WHY WOULD THE RASTER FORMAT REMAIN AN ESSENTIAL PART OF CAD FILE SYSTEMS?
Although raster images not scale up without losing data, they are indispensable for conveying pictorial information and producing animations. The current trend helps store CAD data that leans toward structured file format in which different file formats embed. As each primary CAD format has its right, the raster format undoubtedly remains an essential part of CAD file systems.
What is a raster image in CAD?
Raster and vector are two different approaches used in computer-aided design (CAD), each with its own advantages and applications:
Raster CAD:
Raster CAD works with images composed of a grid of pixels, similar to photographs or scanned images.
It is primarily used for creating and editing images that are based on pixels, such as photographs or digital paintings.
Raster CAD software typically includes tools for editing individual pixels, applying filters, and working with layers.
Common file formats for raster CAD include JPEG, PNG, TIFF, and BMP.
Vector CAD:
Vector CAD works with mathematical equations to define shapes and lines, rather than pixels.
It is used for creating precise drawings and designs that can be scaled to any size without losing quality.
Vector CAD software allows users to create and edit shapes using points, lines, curves, and other geometric primitives.
Common file formats for vector CAD include SVG, DXF, DWG, and AI.
What is a raster image?
A raster image, also known as a bitmap image, is a type of digital image composed of a grid of individual pixels (picture elements). Each pixel contains specific color information, and when arranged together in a grid, they form the visual representation of an image. Raster images are commonly used for photographs, digital artwork, and any other type of image that requires complex color and shading variations.
Key characteristics of raster images include:
Pixel-Based: Raster images are composed of pixels, each with its own color value. The resolution of a raster image determines the number of pixels it contains, which in turn affects the image quality and detail.
Resolution Dependent: Raster images have a fixed resolution, meaning they have a specific number of pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). Changing the size of a raster image can result in a loss of quality if the resolution is insufficient.
File Formats: Common file formats for raster images include JPEG, PNG, TIFF, GIF, and BMP. Each format has its own compression methods and features, suitable for different types of images and purposes.
Editing: Raster images are edited using image editing software like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, or Paint.NET. Editing operations include adjusting colors, adding filters, cropping, and retouching.
Scalability: Raster images are not inherently scalable without loss of quality. Enlarging a raster image beyond its original resolution can result in a loss of sharpness and detail, known as pixelation.