What does CAD Drafting Mean?
It is how one can use CAD or computer-aided design software to create technical drawings and designs. The software’s major aim is to use 2D or 3D tools to create the perfect presentation of models, objects, buildings, machines and even other products. Who can use the same?
Usually, designers, engineers, architects, and other professionals want to use this to get technical drawings precisely and in a time-effective manner. You can use the software to create designs and choose to modify and add new dimensions to the same. Is that all?
You can use the software to generate bills and, at the same time, assemble the final product very easily. The benefits of CAD are far-reaching, and some of the most common ones are cost efficiency, time-saving, accuracy, and productivity!
What Does One Mean By Conversion Of CAD?
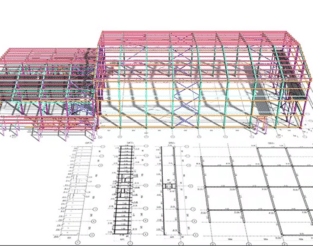
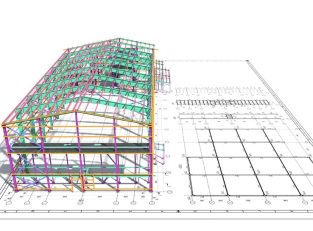
In simplest terms, this uses CAD software and transforms older drawings into completely new digital versions. You save them into CAD files so that they are easily accessible. One generally digitalises the entire painting using specialised software, making it more technical. You can use CAD software for 2D drawings, 3D models, and technical documentation.
For the conversion, you will first need to scan the paper document and then use CAD software, where you manually draw the entire picture. Sometimes, one can make use of the raster to vector technology. This ensures you can get the digital version right from the scanned copy. It usually uses tracing the lines and shapes in the image and then creating a vector-based CAD file.
The conversion process is extremely important across various sectors like manufacturing, architecture, and engineering. These are important in all those sectors where you need to get rid of the older drawings and transform them into more digital versions. It is also extremely easy to handle the document and share the digital version among the other members of the team. CAD conversion has a lot of amazing benefits, including increased accuracy and efficiency, accessibility to important documents and similar others.
Advantages of CAD Drafting and Conversion Services
1. Accurate and Precise
The CAD conversion is the best way to create accurate and precise drawings. It allows you to get the most precise measurements and reduces the chances of making mistakes. It will enhance the quality of your end product.
2. Time Effective
The CAD conversion process is also a great way to save time. It is much less than the time you originally needed to create such precise and detailed technical drawings. It can automatically help you to enhance the production process and increase the productivity manifold.
3. Cost Effective
You can reduce the cost, which comes with manual handling and is often quite a bit. This usually includes indispensable expenditures like the cost of physical materials, labour charges, and the chances of going through a rework if there is any potential damage.
4. Better Visualisation
When we talk about CAD conversion, the given end product is a much enhanced 3D version that helps you get the perfect model. It will help you get the designs to life and allow the clients to better understand what the product will look like.
5. Enhanced Collaboration
And finally, this can help you to enhance the levels of collaboration as well between the difficult members of the team. You can easily share the digital drawings, which will be preserved in the process. You will also not need to meet physically for any kind of meeting or review and can conduct the same online.Conclusion
The CAD conversion process offers many amazing advantages and makes the drawings precise and detailed. It is one of the effective and cost-efficient ways to render desired production. The process is best for those who want to finish technical drawings in a relatively shorter period.
What is the CAD drafting process?
The CAD drafting process refers to the creation of technical drawings using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. Here’s a general outline of the process:
Gather Requirements: Understand the requirements of the project, including dimensions, materials, tolerances, and any specific standards or regulations that need to be followed.
Create Sketches or Conceptual Drawings: Before diving into CAD software, many drafters start with hand-drawn sketches or conceptual drawings to explore design ideas and layout possibilities.
Start CAD Software: Open the CAD software and set up the drawing environment according to the project requirements, including units of measurement, grid settings, and layers.
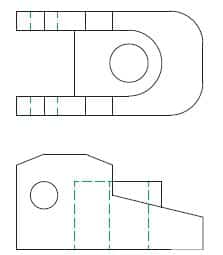
Create Basic Geometry: Use tools within the CAD software to create basic geometric shapes such as lines, arcs, circles, and rectangles. These shapes form the foundation of the drawing.
Construct Objects: Use the basic geometric shapes to construct more complex objects by combining, intersecting, or subtracting shapes. This involves using tools like trim, extend, fillet, and chamfer.
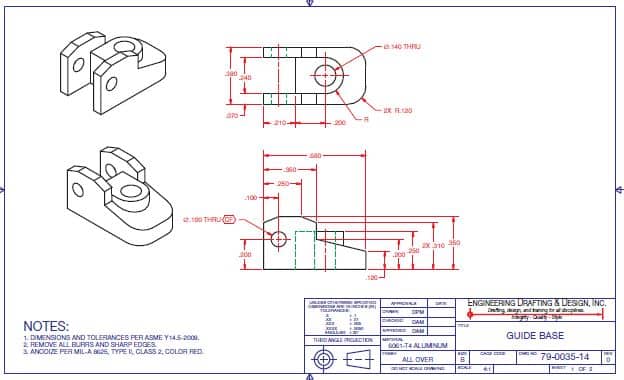
Add Dimensions and Constraints: Dimension the drawing by adding linear, angular, and radial dimensions to define the size and location of objects. Constraints may also be applied to maintain relationships between objects.
Apply Annotations and Text: Add text, labels, symbols, and other annotations to provide additional information about the drawing, such as part numbers, materials, or assembly instructions.
Detailing and Section Views: Create detailed views and section cuts to provide a closer look at specific areas of the drawing, showing internal features or hidden components.
Check for Errors: Perform checks to ensure the drawing is accurate and meets the specified requirements. This may involve verifying dimensions, tolerances, and adherence to standards.
Finalize and Save: Once the drawing is complete and error-free, finalize it by arranging the layout, adding a title block, and saving it in the appropriate file format.
What are the three types of drafting?
The three types of drafting commonly referred to are:
Technical Drafting: This type of drafting involves creating detailed drawings based on specific dimensions, measurements, and technical specifications. It’s commonly used in engineering, architecture, and manufacturing to communicate design ideas and specifications.
Artistic Drafting: Also known as freehand drawing, this type of drafting involves creating drawings or sketches by hand without the use of drafting tools like rulers or protractors. It’s often used in art, illustration, and conceptual design.
Computer-Aided Drafting (CAD): CAD drafting involves using specialized software to create precise and detailed drawings on a computer. CAD software allows for greater efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility compared to traditional drafting methods. It’s widely used in various industries such as architecture, engineering, and product design.