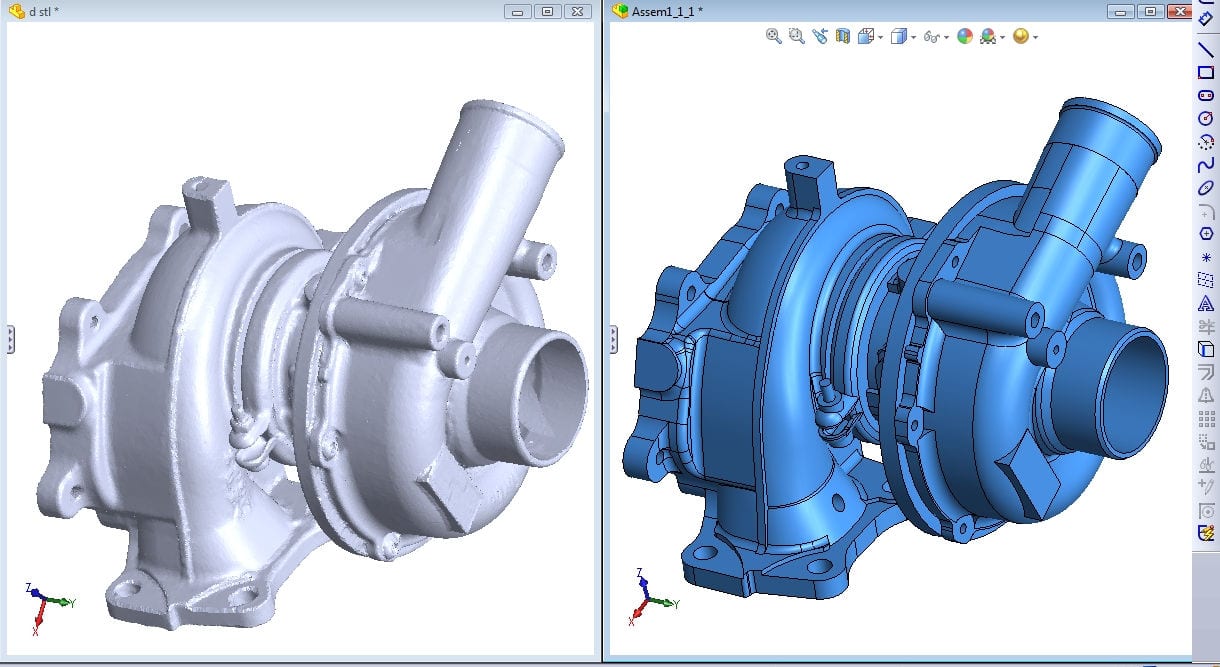
Converting Raw Point Clouds into CAD Formats:
FILES BROUGHT INTO PARAMETRIC MODELERS
Processing 3D data into polygonal models and dumb solids adds a simple mesh file for geometry features that enables to redesign process. It categorised the processing of collected data into two main categories: reverse engineering and Digital Modelling. Digital Modelling uses these simpler model formats that we call Reverse Engineering.
- Reverse Engineering:It’s the process of measuring and creating a CAD model of an object that reflects how the object designed initially been.
- Design Intent:The intended design comes with an in-built physical object where the manufactured part varies from its original intended design. The imperfections can be identified, well-analysed, and corrected using reverse engineering.
- As-Built:The modelling captures the physical shape of an object that actually comes with its imperfections.
WHEN SHOULD ONE REQUEST A PARAMETRIC MODEL VS. THE SIMPLER RAPID NURBS OR POLYGONAL MESH MODEL?
When any project falls into the category of Reverse Engineering, is it opposed to Digital Modelling? Why one should opt for Reverse Engineering, which sounds time-consuming, requires additional processing, and is probably more expensive?
Our recommendation depends on many factors that include shapes such as organic vs. geo metrics to get desired file output. If you’re seeking to make a Rapid Prototype of a hand-carved chair seat, then doing digital modelling can be an excellent option for you. If you scan an aeroplane that creates an accurate model for CFD analysis, you need a model for flow analysis. It comes with an engine casing to redesign and spend the time and effort required to create a fully reversed engineered model.
The desired file output is the main difference between Digital Modelling and Reverse Engineering. People select Digital Modelling for using the file, Rapid Prototyping or visualisation purposes. One needs to redesign purposes for importing models into analysis programs that choose Reverse Engineer, which brings files into parametric modelling software. It essentially adds four types of models.
A Rapid NURBS starts with adding a polygonal model. The NURBS surfaces can be wrapped over the polygonal mesh. The wrapped surface model works more smoothly than a polygonal model with no regular geometric features. This type of NURBS model brought into parametric modellers, which we call dumb.
The bridge between Digital Modelling and Reverse Engineering is called Hybrid Model. Where a hybrid model and polygonal model convert into a rapid NURBS surface model that uses traditional solid modelling techniques. It’s used to add basic geometric features to cover holes & edges, adding complex organic contours.
The Hybrid model steps up fully Rapid NURBS for both time and effort. It is not as time-consuming and comes with an entirely reverse engineered parametric model. Unlike the Rapid NURBS, which wraps around a polygonal frame, the hybrid dumb solid contains geometric features, including holes, planes, and radii, adding features with no parametric history. While an entirely reverse engineered Parametric Model offer fully functional features that allow complete redesign. The models are built from scratch, making them perfect for the reverse engineering of legacy parts and redesigns.
DESIGN INTENT OR AS-BUILT?
When choosing a reverse engineer part, deciding if the part is reverse engineered as-built with its design intent is essential. It comes with physical production parts that are fractions of millimetres and worn down a bit from the original fabrication. It’s necessary to clarify the end use of the data by discussing your project with a reverse engineering firm.
THE REVERSE ENGINEERING ADVANTAGE
It comes with the fine line between Digital Modelling and Reverse Engineering. Both methods come with a valid solution to 3D problems. Few advantages of Reverse Engineering include:
Parametric Modelling Packages covering solid modelling CAD software
Parametric Models feature tree that can editable.
Few other Rapid NURBS dumb solids, reverse engineered models contain geometric features covering planes and radii that make the models a better fit to measure and design.
Reverse engineered models come with excellent analysis software for CFD and FEA.
GETTING STARTED
Direct Dimensions include:
- Geomagic
- Image ware
- Innovmetric PolyWorks
- Rapidform
The CAD packages frequently cover AutoCAD, CATIA, SolidWorks, Siemens NX, ProEngineer, and Rhino3D.
WHAT ELSE CAN I DO WITH A MODEL?
Now that you know about Digital Modelling and Reverse Engineering, you may feel like you don’t need anything else to create 3D models. If you want to make use of the 3D model, Contact Australian Design & Drafting Services to resolve your query.
What is the Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a product or system to understand its design, functionality, and operation. This is typically done by disassembling or deconstructing the product to uncover its internal components, structure, and logic. Reverse engineering can be applied to various fields including software, hardware, mechanical systems, and even biological systems.
In software, reverse engineering involves examining a compiled program’s code to understand its algorithms, protocols, and data structures. This can be useful for understanding how a program works, fixing bugs, or creating interoperable systems.
In hardware, reverse engineering might involve dismantling a device to understand its circuitry, components, and manufacturing processes. This can be useful for understanding how a device functions, replicating it, or improving upon its design.
Reverse engineering is often used for competitive analysis, product improvement, compatibility testing, and ensuring interoperability between different systems. However, it’s important to note that reverse engineering may involve legal and ethical considerations, particularly when it comes to intellectual property rights and proprietary information.
What are the 5 steps of reverse engineering?
The process of reverse engineering typically involves several key steps:
Initial Analysis: This step involves gathering information about the product or system to be reverse engineered. This may include studying its specifications, functionality, and behavior. Understanding the purpose and goals of reverse engineering is crucial in this phase.
Decompilation or Disassembly: In this step, the product or system is broken down into its individual components or parts. For software, this may involve decompiling the code to understand its structure and logic. For hardware, it may involve disassembling the physical components to examine their design and functionality.
Understanding Functionality: Once the product or system has been decompiled or disassembled, the next step is to analyze its functionality. This involves identifying how the components interact with each other and how they contribute to the overall operation of the system.
Documentation and Analysis: During this step, the findings from the reverse engineering process are documented. This documentation may include diagrams, flowcharts, or written descriptions of the system’s architecture, algorithms, and protocols. Analysis of the system’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential improvements may also be performed.
Reconstruction or Replication: Depending on the goals of the reverse engineering process, the final step may involve reconstructing or replicating the product or system. This could involve creating a new version of the software or hardware based on the insights gained from the reverse engineering process. Alternatively, it could involve creating interoperable systems or developing improvements or modifications to the original product.