Engineering design and drawing offer a broad subject that includes many theories and practices. It has different forms of drawing at the lunch table as a basic sketch of a new product idea drawn on a napkin.
Additionally, the drawing comes in the form of a complex series of models for a new automotive design. It uses hundreds of formal drawings that require the construction of a skyscraper. One could learn the purpose and requirements and create meaningful engineering drawings by using this textbook to study engineering drawing and design. The engineering design applications offer an early explanation along with systematic problem-solving techniques.
WHAT IS THE ENGINEERING DESIGN APPLICATION
We use specific engineering projects or general design along with drafting concepts. The engineering design application mainly uses post guides through a basic example of an engineering design process. It begins with an idea and a basic sketch that ends with manufacturing an actual product.
From an Idea to a Product
The engineering projects and design ideas establish or occur along with an informal setting. For instance, a hand-tool manufacturing company engineer uses a typically adjustable wrench to complete a common home-repair task.
They used the wrench, where the engineers discovered that it was difficult to access a confined location and remove a nut on a piece of equipment. The engineer additionally imagined how the company could manufacture, design, and market a new wrench. We use features that help in making the tool usable in cramped locations. The other day, the engineer and a colleague used the drafting department. The engineer mainly sketches the idea for the new wrench on a napkin by communicating the design to the drafter.

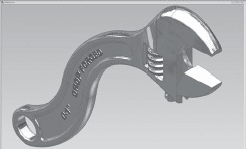
The sketch mostly shows the idea of taking the existing tool design that creates a whole new handle adding an ogee or S-shaped curve design. Additionally, the sketch communicates the concept that takes a current tool with creating a fresh hold of an S-shaped curve design.

Later the same day, the drafter would offer the three-dimensional (3-D) solid model files using existing wrench design based on the computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) system.
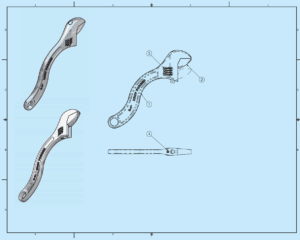
The user mainly uses drafter copies that revise the existing design based on the engineer’s sketch. The drafter represents the engineer’s new model, who is pleased with the results and requests of a rapid prototype. Rapid prototyping (RP) is a process that creates a physical and functional model from a computer-generated 3-D model. It uses an RP machine, known as a 3-D printer. The RP machines are available that build prototypes from various materials like paper and liquid polymer. The hand-tool company do not have an RP machine. Therefore, the drafter sends files of the design to a company specialising in RP. The engineer and drafter receive a prototype two days later.

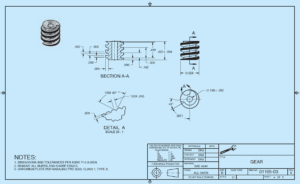
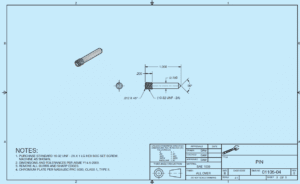

WHAT IS THE ENGINEERING DESIGN APPLICATION
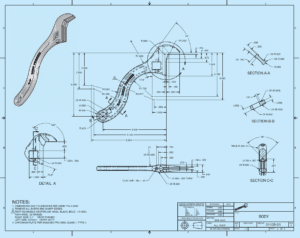
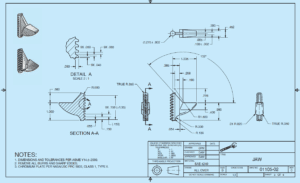
We have the best design team that tests the prototype in an application. It works similar to what the engineer experienced at home. The prototype worked as expected. The drafter supports along with completing the set of working drawings by the next day and sends the drawings to the manufacturing department. It helps to manufacture and assemble the new product. The manufacturing department needs lead time to design and make the forging dies required to reproduce the parts. The Lead time is the time interval between the initiation and the completion of a production process. It helps in the process of shaping malleable metals that presses between dies and duplicate the desired shape. Additionally, the hand-tool company is relatively small. It helps to draft for creating catalogue art and add copy for the product marketing.
Engineering design applications offer numerous benefits that significantly contribute to the efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in the engineering field. Some of the key benefits include:
- Efficiency and Productivity: Engineering design applications streamline the design process, reducing the time and effort required to create complex models. They enable engineers to work faster and more efficiently, leading to increased productivity and shorter project timelines.
- Cost Savings: By using design applications, engineers can identify potential issues early in the design phase, minimizing costly errors and rework. This proactive approach helps save money throughout the entire project lifecycle.
- Improved Design Quality: Engineering design applications allow for more precise and detailed modeling, leading to higher-quality designs. They offer advanced simulation and analysis tools that help engineers optimize their designs and ensure they meet performance requirements and safety standards.
- Collaboration and Communication: Design applications often facilitate collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, as multiple engineers can work simultaneously on the same project. It improves communication between team members and stakeholders, enhancing project coordination and reducing misunderstandings.
- Innovation and Creativity: These applications foster creativity and innovation by providing engineers with tools to explore various design options and alternatives quickly. They can experiment with different concepts and assess their feasibility before selecting the best approach.
- Visualization and Virtual Prototyping: Design applications offer 3D modeling and visualization capabilities, allowing engineers to create realistic virtual prototypes. This enables stakeholders to visualize the final product before physical manufacturing, making it easier to make informed decisions.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: With the ability to simulate and analyze designs, engineers can evaluate the environmental impact of their projects. They can optimize designs to be more sustainable and eco-friendly, aligning with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility.
- Rapid Prototyping and Manufacturing: Many design applications integrate with 3D printing and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies. This integration facilitates the seamless transition from design to physical prototype or production, accelerating the manufacturing process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Design applications often include features that help engineers adhere to industry regulations and standards. They assist in documenting and validating designs to meet legal and safety requirements.
- Continuous Improvement: Engineering design applications often receive updates and improvements, incorporating user feedback and advancements in technology. This ensures that engineers have access to the latest tools and features to continuously enhance their design processes.
Australian Design & Drafting Services provide excellent service for CAD Design and Drafting. Contact Us for more info
Is engineering design a good career?
Engineering design can be a highly rewarding career for those who enjoy problem-solving, creativity, and innovation. Here are some reasons why it can be a good career choice:
Creativity and Innovation: Engineering design involves creating solutions to real-world problems, which requires creative thinking and innovation. It allows engineers to apply their technical knowledge in unique ways to develop new products, systems, or processes.
Variety of Industries: Engineers can work in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, healthcare, and renewable energy, among others. This diversity offers opportunities for specialization and career growth.
High Demand: As technology continues to advance, there is a growing demand for engineers with expertise in design and development. Companies are constantly seeking skilled professionals who can design innovative solutions to stay competitive in the market.
Impactful Work: Engineering design can have a significant impact on society by improving quality of life, advancing technology, and addressing global challenges such as sustainability and healthcare.
Challenging and Rewarding: Designing complex systems or products often involves overcoming technical challenges and working in multidisciplinary teams. Successfully bringing a design from concept to reality can be immensely rewarding.
What are the steps of engineering design process?
The engineering design process typically involves several iterative steps aimed at developing a solution to a problem. While different sources may break down the process into slightly different steps, here’s a commonly accepted framework:
Identify the Problem: Define the problem or need that the design will address. This step involves gathering information, analyzing requirements, and understanding constraints.
Research and Brainstorming: Conduct research to gather relevant data and information. Brainstorm potential solutions and explore various concepts and ideas.
Conceptual Design: Develop initial concepts or sketches based on the research and brainstorming phase. Evaluate different design alternatives and select the most promising ones for further development.
Detailed Design: Refine the selected concepts into detailed designs. This step involves creating technical drawings, specifications, and models to fully describe the proposed solution.
Analysis and Evaluation: Perform analysis and simulations to assess the performance, feasibility, and reliability of the design. This may involve testing prototypes, conducting simulations, or using mathematical models to evaluate different aspects of the design.
Prototype Development: Build prototypes or mock-ups of the design to test its functionality and performance in real-world conditions. Prototyping helps identify any issues or improvements needed before finalizing the design.
Testing and Validation: Conduct testing to verify that the design meets the specified requirements and performs as intended. This may involve various types of testing, such as functional testing, stress testing, and usability testing.
Iterate and Refine: Based on the test results and feedback, refine the design as necessary. Iterate through the design process, making improvements and adjustments until the desired outcome is achieved.
Documentation and Reporting: Document the design process, including all decisions, iterations, test results, and revisions. Prepare reports, technical documentation, and presentations to communicate the design solution to stakeholders.
Implementation and Production: Once the design is finalized and approved, prepare for implementation or production. This may involve coordinating with manufacturers, suppliers, and other stakeholders to bring the design to fruition.
Maintenance and Support: After the design is implemented or deployed, provide ongoing maintenance and support as needed. Monitor the performance of the design and address any issues that arise during operation.
