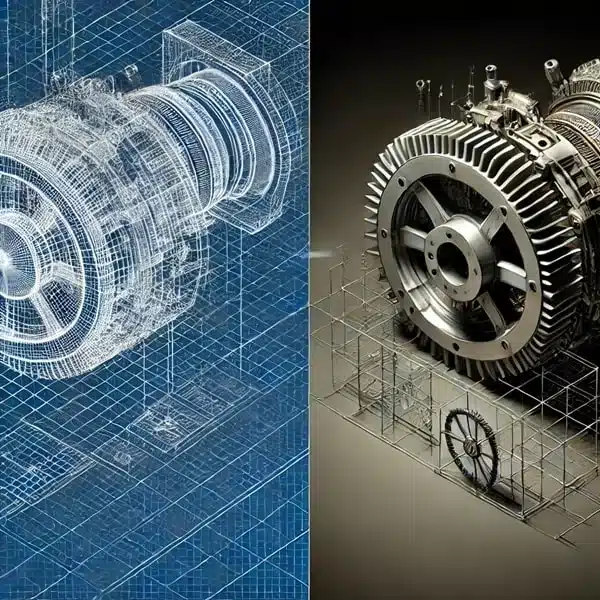
The demand for 2D to 3D conversion is growing rapidly across industries, from architecture to manufacturing. Converting 2D drawings into accurate 3D models is essential for enhancing visualization, improving design accuracy, and streamlining production. However, even experienced professionals can encounter challenges that may hinder the conversion process. To help you achieve flawless results, we’ve compiled expert tips on how to avoid common pitfalls in 2D to 3D conversion services.
2D to 3D Conversion Service
1. Misinterpreting 2D Data
One of the most frequent mistakes during 2D to 3D conversion is misinterpreting the 2D drawings. In 2D designs, some features may be implied through symbols or lines that don’t translate directly into a 3D model. Ensuring a thorough understanding of the 2D blueprint is critical before conversion.
Tip: Carefully review all 2D documentation and engage with the designer or client to clarify ambiguous areas. If necessary, annotate the 2D drawings with notes on how specific details should be modeled in 3D.
2. Overlooking Scale and Proportions
A lack of attention to scale and proportions during the conversion process can lead to major inaccuracies in the 3D model. Misalignment between the 2D design’s scale and the intended real-world dimensions can result in significant rework.
Tip: Verify that the scale in the original 2D drawing is accurate and consistent throughout the design. During the conversion process, ensure that the proportions remain true to the original scale. This is particularly important for complex projects like architectural designs or precision engineering models.
3. Choosing the Wrong Software
The choice of software for 2D to 3D conversion services plays a crucial role in the accuracy and efficiency of the conversion process. Using incompatible or outdated software can introduce errors and slow down the workflow.
Tip: Select specialized software tailored to your industry’s needs, whether it’s AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Revit, or another platform. Ensure that your software supports seamless integration of 2D and 3D elements. Regularly update your tools to take advantage of the latest features.
4. Failing to Optimize Geometry
Converting a 2D drawing into a 3D model without optimizing the geometry can lead to excessive detail or unnecessary complexity in the final model. Overly complex geometry can cause file size issues and complicate manufacturing processes.
Tip: Simplify the geometry wherever possible while maintaining accuracy. Remove redundant details that do not contribute to the functionality or aesthetic of the final 3D model. Streamlining the design can lead to faster rendering and easier modification.
5. Ignoring Design Intent
A common pitfall is focusing solely on the technical conversion of 2D to 3D while overlooking the overall design intent. Misinterpreting how the 3D model should look or function can lead to a final product that doesn’t align with the project’s objectives.
Tip: Always keep the design intent in mind during the conversion process. Collaborate with stakeholders to ensure that the final 3D model meets the design’s functional and aesthetic goals.
6. Lack of Collaboration with Experts
Attempting to handle 2D to 3D conversion without the guidance of skilled professionals can result in costly errors. Conversion requires a combination of technical expertise, industry-specific knowledge, and precision.
Tip: Work with experienced 2D to 3D conversion services to ensure that the process is handled efficiently and accurately. Professional services can offer valuable insights, reduce conversion time, and eliminate errors that may arise from misinterpretation.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common pitfalls in 2D to 3D conversion can help you achieve flawless results and enhance the overall quality of your projects. By paying attention to detail, selecting the right software, and collaborating with experts, you can streamline the conversion process and produce accurate, functional 3D models. When in doubt, partnering with a reliable 2D to 3D conversion service like ASTCAD can ensure that your project is in capable hands, delivering exceptional outcomes with minimal hassle.
What is the process of 2D to 3D image processing?
The process of 2D to 3D image processing involves converting a flat, two-dimensional image into a three-dimensional representation. This is used in various fields such as medical imaging, animation, gaming, architecture, and more. The process typically follows these steps:
1. Image Collection
The first step is gathering the necessary 2D images, drawings, or scans that will be used for conversion. These could be technical drawings, photos, or medical scans (like MRIs or CTs), depending on the application.
2. Image Preprocessing
Before conversion, the 2D images are cleaned up and optimized for better accuracy in the 3D model. This might include:
Enhancing contrast or brightness to highlight features.
Noise reduction to remove unwanted artifacts.
Edge detection to define boundaries and contours more clearly.
This step ensures the image quality is sufficient for accurate 3D rendering.
What is 3D image processing techniques?
3D image processing techniques involve methods and algorithms that analyze, manipulate, and enhance 3D images or data to extract valuable information or create detailed visual representations. These techniques are widely used in fields such as medical imaging, computer vision, virtual reality, robotics, and scientific research. Below are the key techniques involved in 3D image processing:
1. 3D Reconstruction
This technique converts 2D images or slices into a 3D model by estimating depth and structure. It’s often used in medical imaging (like CT and MRI scans) or computer vision. Common methods include:
Stereoscopic reconstruction: Using two images from different viewpoints to build a 3D model.
Shape-from-shading: Infers depth from lighting and shading in a single 2D image.
Photogrammetry: Creates 3D models from a series of photographs taken from different angles.
2. Point Cloud Processing
A point cloud is a set of data points in 3D space representing the external surface of an object. Processing point clouds involves:
Registration: Aligning multiple point clouds from different angles or positions into a unified coordinate system.
Downsampling: Reducing the number of points while maintaining the object’s shape to optimize processing.
Segmentation: Identifying and separating meaningful parts of the object from the point cloud.