Computer Aided Engineering
The computer-aided engineering (CAE) method mainly uses computers to analyse, design, and manufacture a product, project, and process. CAE relates to elements of CADD in industry. CAE often work as a recognised umbrella discipline that involves a lot of computer-aided technologies that are not limited to CAD, computer-aided industrial design (CAID), CNC, CAD/CAM, PDM and CIM, plus the Internet and other technologies that collaborate on various projects. Talking about CAE it often focuses on mechanical design and product development automation.
Its most familiar elements of CAE where simulation and solid modelling, analysis, optimisation and testing of mechanical structures. It adds a system that uses digital prototypes. FEA is a kind of process that is often associated with Computer-Aided engineering.
DESIGN APPLICATION
Computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) service companies relate to computer-aided technologies that offer revolutionary tools for engineers and drafters during the engineering design process. CADD enhances design efficiency, creativity, and effectiveness in product development. There are a lot of different forms that accept engineering design processes and integration of CADD within the engineering design process. Get a simplified sample of an engineering design process for a lifting hook.
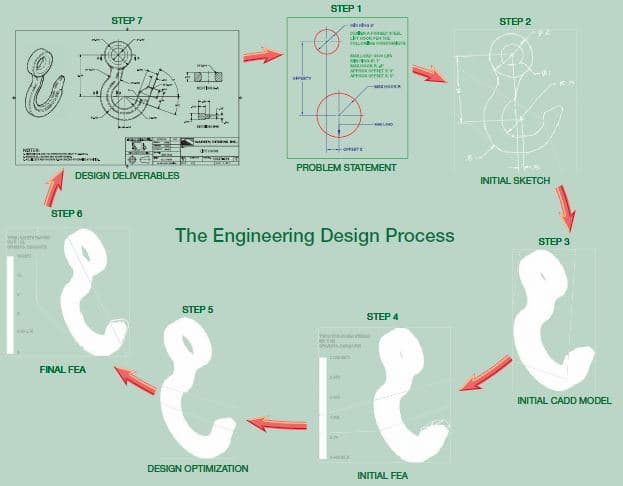
The lifting hook is one best example, and the following information is an introduction to CADD in the engineering design process.
STEP – 1
Step 1 helps to identify the problem along with adding design constraints. It comes with a constraint and a condition adding a specific shape, size, or requirement. It defines a design that satisfies to achieve a successful design. The problem statement describes the requirements and constraints for a forged-steel lift hook that support a 3000-pound load.
STEP – 2
Step 2 offers a sketch of the initial design based on the solution to the problem. The sketch comes with hand-drawn that use CADD as a sketching tool. CADD systems require the creation of a digital sketch as an element of the CADD process. The hand-drawn sketches come with a common practice that especially comes during early design.
STEP – 3
Step 3 can generate an initial three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) solid model according to the hand-drawn sketch. Using finite element analysis (FEA) software, you can study the model. Here, FEA applies the finite element method (FEM) to solve mathematical equations related to engineering design problems, including structural and thermal issues.
STEP – 4
Step 4 offers structural stress analysis applied to that lifting hook to simulate a real-world lift.
STEP – 5
Step 5 optimise the design to reduce material with improving shape while maintaining a sufficient working strength. Users can perform design optimisation, adding manual calculations and tests and repeated FEA simulations. It offers an optimised lift hook with CAD solid model.
STEP – 6
Step 6 can re-analyse the model that confirms a solution to the design problem.
STEP – 7
The last step 7 is to use the CAD solid model to prepare two-dimensional (2-D) detail drawings and a digital model format supported by computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. The manufacturer mainly uses the supplied data to create the forging equipment necessary to produce the lifting hook.
PROFESSIONAL APPROCHED
A wide variety of jobs are currently available for qualified CADD professionals. Note that the kinds of tasks they may allow is always traditional. In addition to this, they create drawings that are responsible for working in some of the following areas, including:
- To prepare freehand sketches on the shop floor and convert the sketch with finished CADD drawing.
- To include Digital image creation and editing.
- To provide text documents, including proposals, reports, and studies.
- To incorporate CADD images and drawings into text documents.
- To conduct research for job proposals, purchasing specifications and feasibility studies.
- To evaluate and test new software with ease.
- To train the staff members by using new software or procedures.
- To collect vendor product information for new projects.
- To speak on the phone and deal personally with clients, vendors, contractors, and engineers.
- To check design and drawings by creating accuracy.
- To research computer equipment and prepare bid specifications for purchase.
Computer Aided Engineering
We often hire employees who possess good tech skills to become good employees. The best jobs that we can find here are those students who developed an excellent understanding of the project planning process and can easily handle any situation.
The process is based on the person’s ability to communicate. It helps to apply solid math skills through trigonometry with exhibiting good problem-solving skills. We know how to use resources and conduct research by getting all data. We can serve general qualifications foundation by adding more specific skills to our study. It includes good working knowledge of drawing layout and construction techniques. Based on applicable standards, it adds a good grasp of CADD software mainly used for creating models and drawings.
In addition, we support you in customising the CADD software that better suits your needs. What is most essential for the prospective drafter to remember. Content applies to the lot of details of an object, situation and procedure. If we are given enough time, then we can find all of the pieces of information required to complete a task.
Here the process refers to a method of doing something. It involves several steps that come with learning a helpful process and making it easier to complete all tasks. We can find all of the content you require and understand an exemplary problem-solving method. It comes with project planning and is used in any situation. We can use the process to make the task easier and determine what content would be beneficial.
There are many more reasons that we strongly recommend you focus on your efforts. We learn and establish good problem-solving habits. Using the skills to locate the content, all we need for any project is to make all aspects of your life productive, efficient, and relaxing. We at Australian Design & Drafting Services company are ready to offer excellent CAD Design and Drafting services. Contact Us to give wings to your project.
What is difference between CAD and CAE?
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) are both integral parts of the product development process, but they serve different purposes.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design):
– CAD software is primarily used for creating 2D or 3D digital models of products or parts.
– CAD tools are focused on facilitating the design and drafting process, allowing engineers and designers to visualize and develop concepts.
– CAD software enables precise geometric modeling, drafting, and annotation of designs.
– It’s commonly used in industries like architecture, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods for creating product designs, architectural plans, and engineering drawings.
CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering):
– CAE software is used to simulate and analyze how products will perform under different conditions.
– CAE tools allow engineers to perform virtual testing, optimization, and validation of designs before physical prototypes are built.
– CAE encompasses various types of analyses including structural analysis, thermal analysis, fluid dynamics (CFD), and electromagnetic simulation.
– It helps in understanding product behavior, identifying potential issues, and optimizing designs to meet performance criteria and regulatory standards.
– CAE is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, energy, and manufacturing for design validation and optimization.
What does a CAE engineer do?
A CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) engineer utilizes computer software and simulations to analyze, simulate, and optimize engineering designs and processes. Their responsibilities often include:
Simulation and Analysis: They use specialized software to simulate how products or systems will perform under different conditions. This could involve stress analysis, fluid dynamics, thermal analysis, or electromagnetics depending on the field.
Design Optimization: They work to optimize designs to meet specified criteria such as performance, efficiency, safety, or cost-effectiveness. This involves running simulations with different parameters to find the best design solution.
Product Development Support: CAE engineers often collaborate closely with design engineers to provide insights and feedback during the product development process. They may suggest design modifications based on simulation results to improve performance or reduce potential issues.
Validation and Verification: They validate and verify designs through simulation, ensuring that they meet industry standards, regulations, and customer requirements before physical prototypes are built.
Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: CAE engineers may investigate and troubleshoot issues that arise during product development or in existing products/systems, using simulation tools to diagnose problems and propose solutions.
Research and Development: They contribute to ongoing research and development efforts within their organization, exploring new simulation techniques, software tools, or methodologies to improve the engineering design process.
